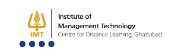Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship: Two Sides of the Same Coin?
The terms entrepreneur and entrepreneurship are being used interchangeably and everyone has heard of them. But do you know that these terms do not mean the same thing? If not, you are not alone! Most people think that they are similar, but in fact, they are not. It is extremely important to realize this difference, particularly for individuals who have aspirations to become an entrepreneur and simply want to get through the startup and innovation world.Just think of it: an entrepreneur is human, an individual who assumes risks, develops concepts, and establishes companies. But, entrepreneurship can also be termed as the journey, process and all that goes on while turning the idea successful. Thus, it can be stated that one is the driver, and the other is the path they drive on.
In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between an entrepreneur and entrepreneurship, explore their characteristics, and understand how they shape the business world. So, if you are wondering what truly sets them apart, let’s explore!
Entrepreneur vs. Entrepreneurship: An Overview

At first sight, entrepreneur and entrepreneurship could pass as two words for the same thing, yet they are entirely different. An entrepreneur is a person who spots opportunities, takes risks, and starts businesses. Entrepreneurship is, however, the process by which businesses get to exist and succeed.
Moreover, Entrepreneurs lead the formation of businesses, with the responsibility of making strategic decisions and overcoming obstacles. Entrepreneurship is the whole process required to develop an idea into a successful business, including innovation, utilization of resources, and market positioning.
Though vision and leadership are entrepreneurial concerns, viability and implementation are the entirety of entrepreneurship. Both are the core to economic development, innovation development, employment, and competition. These differences provide a glimpse into why there are businesses and why they survive. Let us discuss it in detail.
Who is an Entrepreneur?

An entrepreneur is an individual who establishes and runs a business enterprise. They spot opportunities in the market, develop creative solutions, and take calculated gambles to initiate and grow their business. Entrepreneurs are known to turn ideas into successful businesses through strategic planning, resource management, and leadership.
Entrepreneurs work in different sectors, ranging from technology and finance to retail and healthcare. They can start new ventures, grow existing companies, or bring about disruptive innovations. Their job entails making key decisions, raising capital, running operations, and responding to changes in the market.
Successful business people usually exhibit traits such as determination, resilience, resourcefulness, and problem-solving. Their impact is not limited to individual achievement but also stimulates economic development, creates jobs, and shapes industry patterns. Entrepreneurship exists in various forms, but all entrepreneurs have the same aim of establishing sustainable businesses.
What is Entrepreneurship?

Entrepreneurship is the process of developing, creating and running a business venture with the objective of earning profit or value creation. Entrepreneurship is the process of making an idea become a successful business through the use of innovation, strategic planning, and risk management. Entrepreneurship refers to covering the entrepreneurial process of building and expanding businesses, whereas entrepreneur refers to a human being, by whom the idea was generated and proposed.
It involves several stages including market research, product development, mobilization of investment, development of activities, and innovation in the era of evolving market forces. Entrepreneurship is not limited to starting a new business, it also includes expanding existing enterprises, launching innovative solutions, and fostering economic progress.
Entrepreneurship plays a critical role in driving industries forward by introducing new products, services, and business models. It exists in various forms, from small-scale businesses to high-growth startups and corporate innovations.
Key Characteristics of an Entrepreneur
There are some particular characteristics of entrepreneurs that enable them to form and maintain successful ventures. They differentiate the successful entrepreneur from the average entrepreneur and are essential to assist in maintaining the entrepreneurial journey.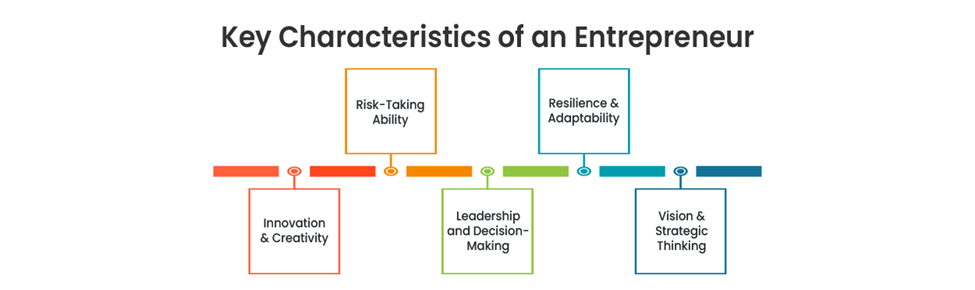
1. Willingness to Take Risks: Entrepreneurs begin with the unknown and make risk determinations without the knowledge of the financial or market outcomes involved. They will consider the situation thoroughly and will then make intentional risk decisions to gain as optimal results as possible.
2. Creativity and Innovation: Successful entrepreneurs think outside the box, creating new products, services or businesses that either resolves an existing issue or creates a new demand in the marketplace.
3. Leadership and Decision-Making: Effectiveness in running a business requires good decision-making. Entrepreneurs motivate teams, assign tasks, and adjust strategies to realize their vision.
4. Resilience and Adaptability: Entrepreneurship involves challenges and failures. Successful entrepreneurs remain steadfast, learn from failures, and change strategies when needed.
5. Vision and Strategic Thinking: Entrepreneurs have vision and strategic thinking. They see what others do not see. They have specific goals, forecast market trends, and create long-term business solutions.
Core Elements of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is certainly more than simply creating a business; it is the process of transforming an idea into a viable long-term business model. There are a number of enablers of the entrepreneurship process that promote long-term success and innovation.
1. Identifying Opportunities: Gap analysis and understanding of unmet customer needs are the building blocks of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurs conduct research into market trends and customer needs in order to develop viable business ideas.
2. Business Planning: A sound business plan will present the company's mission, vision, objectives, financial forecast and operating plan in a clear manner. It is also a decision-making and resource allocation tool.
3. Innovation and Value Creation: Entrepreneurship is living on innovation—either in new products, improved services, or innovative business models. Value creation is what separates a successful business from others.
4. Risk and Resource Management: Business leaders must use financial, human, and technological resources strategically with the lowest amount of risk-mitigation requirements. Sustainability can be ensured by effective budgeting, proper investment and efficient operations.
5. Market Growth and Execution Strategy: Once the foundation is established, business individuals proceed to develop, nurture, and enlarge a firm. Branded development, promotion, customer acquisition, and adaptation with change in the market space are incorporated in this process.
Major Differences Between Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship
Though entrepreneur and entrepreneurship exist side by side, they are two separate notions of business startup and growth. The following are the key differences that separate them:| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is the individual who establishes and runs a small business. | It is the process of building, beginning, and developing a business. |
| Focus | They are driven by personal vision, leadership, and decision-making. | It is concerned with the whole business environment and overall strategy. |
| Role | The ones who are responsible for innovation, risk-taking, and action. | It includes a series of activities like planning, resource deployment, and scaling. |
| Scope | Limited to the person leading the venture. | A broader definition that includes all aspects of business management. |
| Risk Involvement | Entrepreneurs bear personal financial and operational risks. | Entrepreneurship involves managing business risks and uncertainties. |
| Outcome | Success is measured by individual success and business contribution. | Measured by growth, sustainability, and economic contribution. |
Role of an Entrepreneur in Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs are the core aspect of entrepreneurship. They create ideas by finding opportunities, speculating, and rationalizing resources. There would be no entrepreneurship process without entrepreneurs, as they are the ones who start and sustain business processes.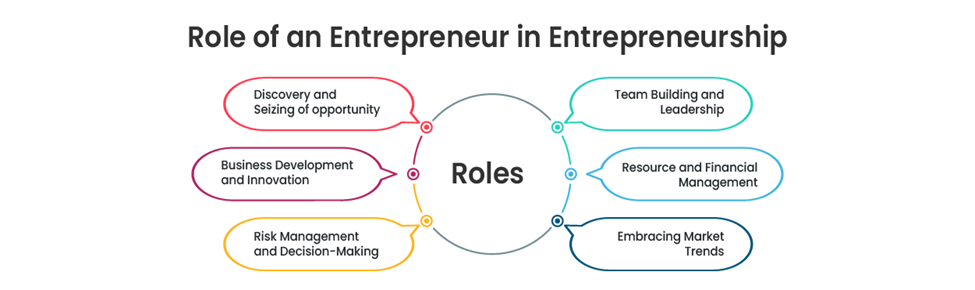
1. Discovery and Seizing of opportunity: The entrepreneur constantly seeks market niches, potential trends, and customer needs. They uncover, scan the needs of industries, and develop new solutions which create value. Detection and grabbing of opportunities are one of the core functions of entrepreneurship.
2. Business Development and Innovation: Entrepreneurs bring about new products, services, or business models to the marketplace that differentiate them from others. They are the agents of entrepreneurship, which brings forth revolutionary innovations in areas like technology, health, and finance. Such innovation leads to growth in the marketplace and economic growth.
3. Managing risk and making decisions: Entrepreneurship is risky, and entrepreneurs make informed decisions to try to advance their business. Entrepreneurs make the critical decisions when investing in assets, moving into new markets, or developing new products, all of which can break or shape the business. Effective risk management offers the long-term stability and sustainability of the business.
4. Team building and leadership: Entrepreneurs do team building and lead people. They engage employees, establish organisational objectives, and build team culture and morale. Entrepreneurship is all about expanding by demonstrating positive leadership through a skilled and motivated workforce.
5. Resource and Financial Management: Entrepreneurship requires the ability to access finances, budget, and resource management. Entrepreneurs seek out investments, investors, and revenue sources to fund and develop the business. Sound financial planning succeeds a business.
6. Embracing Market Trends: Entrepreneurs are required to have the flexibility to adapt to new consumer behavior, technological advancement, and economic trends. Their ability to shift gears and adapt to change ensures continuous growth in entrepreneurship.
In essence, entrepreneurs are at the core of entrepreneurship. They bring their vision, leadership skills, and decision-making capabilities, which make business companies successful and drive economic progress. Entrepreneurship would not be innovative, directionless, or implemented without entrepreneurs.
Impact of Entrepreneurship on the Economy
Entrepreneurship is a key economic growth driver via innovation, job creation, and market expansion in general. Entrepreneurship is a core force behind the development of strong national economies through new business trends creation, productivity, and enhanced market competition. Entrepreneurship impacts are broader than corporations to reach economic and social development on a large scale.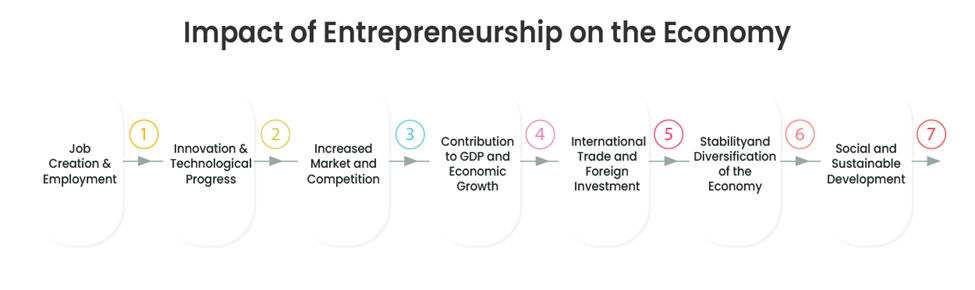
1. Job Creation and Employment: Entrepreneurship significantly contributes to job creation in the form of creating startups and expanding businesses. Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) contribute to generating employment opportunities, diminishing the unemployment rate, and improving the labor force participation rate. As companies expand, they have a ripple effect, leading to an increase in demand for skilled labor and economic stability.
2. Innovation and Technological Progress: Entrepreneurs are responsible for innovation through the creation of new products, services, and processes. Their efforts result in technological innovations that enhance efficiency, lower costs, and raise industry standards. Countries that have a high entrepreneurial spirit are likely to see advances in industries like artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energy, hence becoming more competitive globally.
3. Increased Market and Competition: Entrepreneurship promotes competition by introducing new companies into the market. This forces existing companies to innovate, improve product quality, and offer competitive prices. Consumers are also helped by being able to get better choices, improved services, and lower prices. Increased competition also accelerates economic activity by making companies more efficient.
4. Contribution to GDP and Economic Growth: Entrepreneurs indirectly contribute to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through receipt of income from exports, sales, and business growth. Expanding businesses contribute to national production and thereby to economic growth in the long term. Entrepreneurship helps to grow the economy by encouraging the investment in research and development (R&D) and infrastructure.
5. International Trade and Foreign Investment: An effective entrepreneurial ecosystem draws international investors, foreign multinational companies, and venture capital seeking new opportunities. Foreign investment brings employment prospects, capital, and improved transfer of technology. Entrepreneurial ecosystem is also common in international trade by business expansion across borders, improved export revenues.
6. Stability and Diversification of the Economy: Entrepreneurship discourages dependence on certain industries since it encourages growth in other areas. By stimulating business growth in other sectors, economies are immune to economic crises and market decline. Various industries ensure stability and long-term progress despite economic hardships.
7. Social and Sustainable Development: Today’s entrepreneurs do more than merely making profits; the majority of ventures aim for social and environmental sustainability. Entrepreneurs create sustainable products, operate their business ethically, and develop solutions for social issues e.g. poverty, education, or healthcare. Entrepreneurship leads to a more responsible, inclusive economy.
Challenges Faced by Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurship is fulfilling, yet it comes along with many challenges that stretch an entrepreneur’s resilience, ability to make decisions, and willingness to adapt. Working through challenges is important to the long-term growth and viability of a business.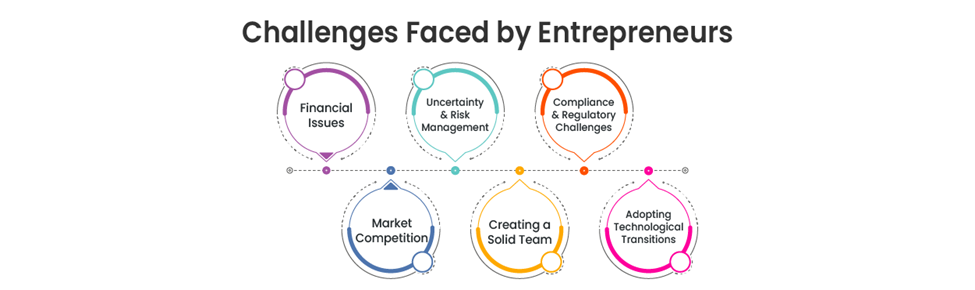
1. Financial Difficulties: One of the most significant challenges entrepreneurs face when launching a business is funding. Some entrepreneurs may not have enough financial history for an investor to be assured. Or, an entrepreneur may attempt to borrow money but must also pay high interest. The lack of funding presents serious challenges associated with scaling to growth initiatives, investing in new business opportunities, and the overall viability of their business to run operations. To tackle their capital problem, entrepreneurs generally use their personal savings, venture capitalists, groups of sources through crowdsourcing, and agencies that provide grants from the local state or federal government.
2. Market Competition: Entrepreneurs must deal with dominant established businesses that have stronger resources, brand recognition, and customer loyalty than new businesses. Entrepreneurs have to figure out how to position their products away from established brands so they can create their market share and remain competitive and influential in their markets. They can do this by providing exclusive value propositions, maintaining good branding, and creating interesting marketing strategies to develop a competitive advantage against competitors.
3. Uncertain market environments and risk management: Entrepreneurs are always faced with a level of uncertainty, as market environments can unpredictably change based on economic conditions, consumer behavior, and industry practices. Entrepreneurs must anticipate business risk and possibilities of monetary loss, operation ineffectiveness, and legal challenges. Entrepreneurs should comprehensively consider potential risks and how they will react, in the apparent event that events unfold into the possibilities of risk. In the same vein, entrepreneurs need to be flexible and have backup plans.
4. Creating a Solid Team: Success of a company lies in its team. Acquisition of good professionals, creating a good work environment, and keeping employees are herculean tasks. Startups have minimum financial means to offer competitive packages, so there is no dearth of challenges in recruitment. Entrepreneurs must focus on leadership, inspiration, and career development to make a loyal team.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Challenges: Startups must deal with complex legal regimes, including registration, taxation, labor laws, and sector regulation. Failure to comply can result in penalties, lawsuits, or shutdown of the business. Staying up to date with legal requirements and seeking professionals' advice can help entrepreneurs comply with regulations.
6. Adopting Technological Transitions: As technology evolves continuously, business masters need to update their business model, digital presence, and process flow on a regular basis. If they do not adopt change, they risk being obsolete. Digitalization, automation, and security investments are the need to stay competitive.
Conclusion
Entrepreneurship is not about starting a company; it's about vision, taking risks, and perseverance. Entrepreneurs form the core of economic expansion, fueling innovation, job creation, and industries' evolution. Entrepreneurship as a process may offer the architecture, but entrepreneurs' passion, leadership, and drive translate into ideas being developed.Naturally, the ride is not always smooth. Capital raising, weathering market competition and legal battles are some of the challenges entrepreneurs must endure. But entrepreneurs who are flexible, willing to innovate and commit to continuous learning will be able to convert failures into success. The reach of entrepreneurship extends far beyond personal achievement—it sets economies on fire, constructs communities, and creates the foundations for future innovation.
So, whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur or simply curious about the world of business, one thing is clear: entrepreneurship is a dynamic force that continues to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most important difference between an entrepreneur and entrepreneurship?
An entrepreneur is a person who initiates and operates a business, while entrepreneurship is the activity of starting, growing, and operating a business. Entrepreneurs create things, while entrepreneurship offers the platform for business development.
2. Can anyone be an entrepreneur?
Yes, if someone has an idea for a business, a desire to do it, and is ready to face the risks along the way, they can be an entrepreneur. Having knowledge or experience is useful, but it is more of a function of problem-solving skills, adaptability and resilience that will determine if you are successful or not in your endeavours.
3. Why is entrepreneurship so vital to the economy?
Entrepreneurship drives economic growth through creating employment opportunities, innovation, competition, and the attraction of investment. Entrepreneurship contributes to GDP and promotes industrial and technological advancement.
4. What are the largest concerns entrepreneurs are facing?
Businesspeople are likely to encounter financial constraints, market competition, managing risk, regulatory compliance, and talent acquisition. Strategic planning, innovation, and resilience are needed to overcome these challenges.
5. In what ways does entrepreneurship foster innovation?
Entrepreneurs bring in new products, services, and business models, pushing industries forward. Their willingness to take risks and be creative results in technological innovations and better solutions for customers.
Trending Posts
-
Top 11 Affordable Online MBA Colleges in India in 2025
-
Top 5 Online Universities in India for Online MBA in Healthcare Management
-
Top 5 Online MCA Colleges in India in 2025
-
How Much Do BCA Graduates Earn? Salary & Career Path Explained
-
How to Choose the Right Stream After Class 10: A Complete Guide
-
Are Online MBA Degrees Valid in India? All You Need to Know About Them
-
Top 10 Online MBA Specializations in Demand in 2025 and How to Choose?
-
A Guide on Dual Degrees: Benefits, How to Get, and Institutes Offering Dual Degrees
-
Top Finance Project Ideas for Career Growth: From Investment to FinTech
-
Parul University Online Programs 2025: Programs, Admission, and Benefits
-
Top Certifications to Boost Your Earnings by 10 Lakhs or More
-
Jamia Millia Islamia Online & Distance Courses 2025 – A Student’s Guide
-
A Guide on Online MBA in Airlines and Airport Management at CU Online
-
Kurukshetra University Online & Distance Learning: Quality Education at Your Fingertips
-
15 Top Online MBA Colleges in India in 2025